
How To Receive Wifi Signal From Long Distance
Learn how to analyze your home's layout, upgrade to better router hardware, strategically place access points and implement signal boosting tools to increase wifi range.
Getting a strong, reliable wifi signal from long distances can be a challenge in large homes or outdoor spaces.
Fortunately, with the right tips and tools, you can optimize your network to maximize range and enjoy seamless internet access even from 100+ feet away.
This comprehensive guide will teach you how to analyze your current setup to identify range limitations, select the optimal router placement, implement signal-boosting extenders and high-gain directional antennas properly, and fine-tune your network settings for long-distance WiFi coverage.
How to Receive WiFi Signal From Long Distance
Show Summary
Improving Wi-Fi signal strength for long distances can be achieved through several strategies:
- Optimal router placement
- Use high-gain directional antennas
- Using WiFi extenders
- Using a Mesh network
- Upgrade Your Router
Strategically Place the Router

Placing your wireless router in a central area of your home is vital for maximizing WiFi range. Signals propagate outwards in all directions from the router, so a central position covers the most area.
According to experts, a centrally located router on an upper floor can increase range by up to 20% compared to a corner location. Range is also improved by 25-50% when elevating the router instead of leaving it on the floor.
Avoid concrete walls and obstructions: Concrete, brick, and plaster walls block WiFi signals and severely limit range. Strategically avoid positioning the router next to or against exterior walls or foundations.
Many routers have removable external antennas that should point vertically outward to propagate the signal. Angling antennas horizontally or downward focuses energy uselessly into the floor or ceiling.
Electronics, water, and microwaves can interfere with WiFi signals. Keep the router away from these sources to minimize interference and maintain a strong connection.
Using High-Gain Directional Antennas
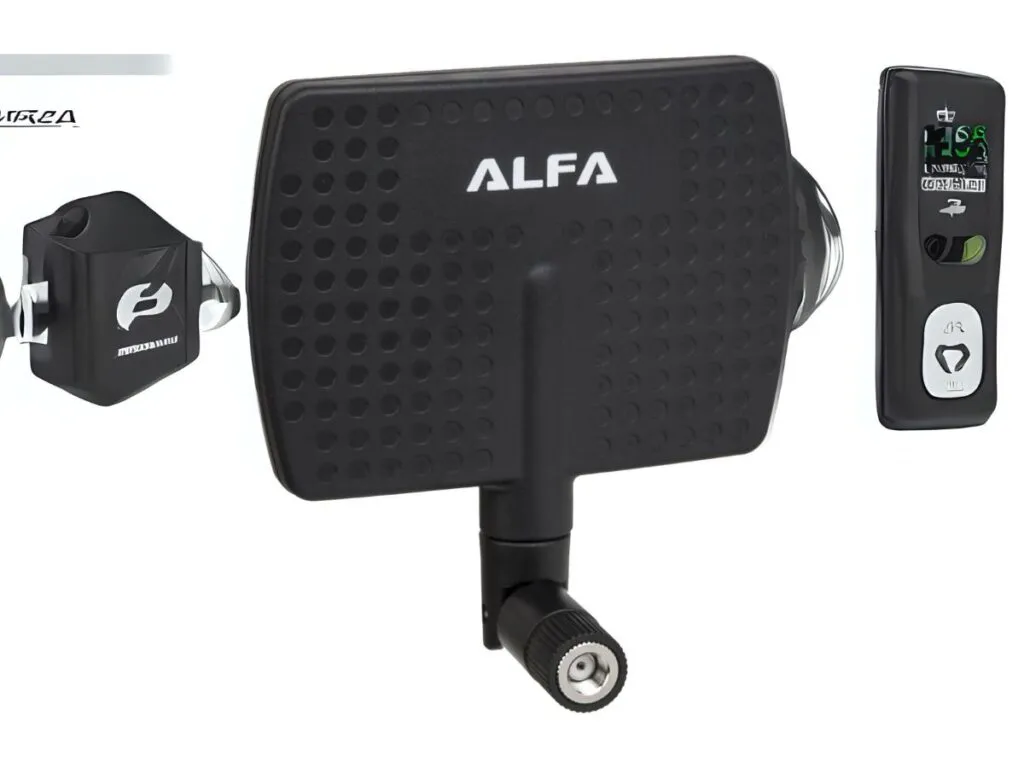

High-gain directional antennas can significantly enhance your ability to receive Wi-Fi signals over long distances. These antennas work by focusing the signal in a specific direction, which can increase performance and reduce signal interference.
High-gain directional antennas work by focusing the Wi-Fi signal in a specific direction, rather than radiating it uniformly in all directions like omnidirectional antennas. This focused approach allows the signal to reach further distances and reduces interference from other signals
There are several types of directional antennas suitable for increasing WiFi range, each with their own characteristics:
- Yagi antennas These very popular directional antennas look like arrows and can achieve 9-15dBi gain. They provide a horizontal beamwidth of around 45 degrees
- Parabolic grid antennas
Extremely directional with gain over 20dBi, these have beamwidths from 4-20 degrees. They are great for point-to-point links - Panel antennas
Compact directional antennas with gain of 10-19dBi and beamwidths around 30-60 degrees. Easy to mount on walls - Dish antennas
Large parabolic dish antennas that can produce narrow beamwidths under 5 degrees. They provide the highest gain of 25-30dBi
By combining high-gain directional antennas in optimal outdoor mounting locations, it is possible to achieve directional WiFi distance of over 5-10 miles.
Examples of high-gain directional antennas include the Alfa 10dBi High-Gain WiFi Antenna and the Waveform MIMO WiFi Antenna.
Use a WiFi Extender

WiFi extenders, also called repeaters or boosters, work by receiving an existing WiFi signal, amplifying it, and rebroadcasting the boosted signal to extend the network’s range. This helps eliminate “dead zones” where the WiFi from your router doesn’t reach.
According to Consumer Reports testing, a WiFi extender placed halfway between a router and a laptop 45 feet away with two floors/walls in between helped provide a strong extended signal to the laptop.
Modern WiFI extenders provide a seamless experience without needing to manually switch networks as you move around the home. Devices automatically connect to the strongest signal from either the router or extender.
The Netgear WiFi extenders, for instance, have “FastLane3” technology to provide a unified network with smooth transitions as you roam for the best possible speeds
WiFi extenders can help you receive WiFi signals from a long distance by extending the coverage of your existing wireless network.
Some of the best WiFi extenders available in 2024 include the TP-Link RE605X, which supports the latest WiFi 6 speeds and features, and the Linksys RE7310.
Using a Mesh WiFi System

A mesh network is a decentralized type of wireless network that consists of multiple nodes or access points that communicate with each other to distribute wifi coverage over a large area. The nodes work together to form a mesh-like topology where data can travel through multiple potential paths to reach its destination.
In a Mesh Network, each node (or device) is connected to several other nodes. If one node drops out of the network, its neighbors simply find another route to transmit data. This makes Mesh Networks highly resilient and reliable.
While a single wireless router may only cover about 100-150 feet indoors, a mesh network can extend a WiFi signal over miles. A Mesh Wi-Fi network can provide a signal covering 2,000 to 5,500 square feet.
Some of the best Mesh WiFi routers available in 2024 include:
- Asus ZenWiFi AX XT8: This router offers speedy performance and impressive range.
- TP-Link Deco X20 AX1800: This is a budget-friendly option that doesn’t compromise on performance.
- Eero 6: This router is recommended for smart homes.
- Netgear Orbi AX4200 RBK753: This router is ideal for large homes
- TP-Link Deco XE75: This router offers Wi-Fi 6E connectivity and is recommended for mesh networking.
Some mesh systems use a dedicated wireless backhaul channel for communication between nodes, avoiding interference and improving penetration.
Using Reflector Panels
Reflector panels are metallic plates, usually made of aluminum, that can reflect and focus WiFi signals in a specific direction.
By angling the reflector panel towards an access point, you can strengthen the signal received from long distances.
A study by the University of Michigan proposed the use of metallic plates, mainly aluminum plates, as reflectors to reduce signal fading. This is because metallic surfaces are excellent at reflecting radio waves, which include WiFi signals.
By positioning a reflector panel in the path of the WiFi signal, you can direct more of the signal toward your WiFi receiver, thereby improving the strength and range of the signal.
Carefully positioned aluminum reflector panels provide a low-cost way to extend your WiFi network’s range.
To use a reflector panel effectively, you need to position it correctly. The panel should be placed in such a way that it captures the WiFi signal and reflects it towards your WiFi receiver. This might require some trial and error to find the optimal position.
There are also commercial products available that incorporate reflector panels into their design. For example, the Alfa Die Cast Reflector is a product that uses a large reflector panel to enhance WiFi reception.
Use Low-Frequency Channels
Wi-Fi networks operate on radio frequency bands - commonly 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Lower frequencies like 2.4GHz travel farther and penetrate obstacles better than higher 5GHz frequencies.
Lower frequency radio waves, like those used on the 2.4GHz WiFi band, are able to travel farther distances and penetrate through walls and obstacles better than higher frequency waves like 5GHz WiFi.
The 2.4GHz Wi-Fi frequency can transmit signals hundreds of feet or more when using directional antennas and clear channel selections like 1, 6, or 11. This makes 2.4GHz ideal for long distance outdoor point-to-point Wi-Fi links.
Most modern WiFi routers support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, but may default to using the higher 5GHz band. Here are some tips to force your devices to use 2.4GHz when available:
- Separate your 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks into different SSIDs and manually connect your long-range devices to the 2.4GHz network.
- Disable 5GHz on your router if you don’t need the extra speed at short range.
- Set the 2.4GHz band as higher priority on devices that support band steering.
- Manually set your devices to use 2.4GHz only. This may require going into advanced WiFi settings.
- Consider using a WiFi extender on the 2.4GHz band to reach farther distances.
Once on the 2.4GHz band, optimize your channel selection to minimize interference. Use a WiFi analyzer app to scan for congestion and choose the least crowded channel (1, 6, or 11).
Factors affecting WiFi Signal Range
-
- Router capabilities: Think of your router as a lighthouse, sending out beams of data that guide your devices through the vast ocean of the internet. Just as different lighthouses have varying intensities of light, routers have different capabilities that determine the strength and range of their signals. Some factors to consider include the router’s power output, frequency bands, and the number of antennas it has.
-
- Environmental Factors: When you’re trying to catch a WiFi signal from a distance, it’s essential to remember that your surroundings play a role, acting like the weather on the open sea. The construction materials of your walls, ceilings, and floors can impede the signal, just as a storm might dampen a lighthouse’s beam. Even the placement of your router within your home or office can affect the signal’s ability to travel far and wide.
-
- Interference from Other Devices: Other electronic devices, like microwaves and cordless phones, can disrupt this delicate dance by introducing interference. It’s as if they are unruly spectators in the audience, creating chaos and confusion, making it difficult for your devices to pick up the WiFi signal clearly.
Limitations of standard WiFi networks
Standard WiFi networks, like the ones most of us have in our homes or offices, have a limited range by design. Typically, a standard router can cover an area of up to 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors. While this is often sufficient for small to medium-sized spaces, it can leave you stranded in a digital desert if you need to connect from a greater distance.


What is a long-range WiFi network and how does it work?
Long Range wifi
Most individuals need dependable internet access in all areas of their houses and other properties. In most circumstances, the bigger the property and the more structures there are, this is more difficult and expensive. Problems occur when you combine that with rural homes which do not have well-established Internet infrastructure.
There is a different option. WiFi long-distance networks can assist in improving internet connectivity in a specific region or temporarily extend WiFi signals outside the building.
Receiving WiFi Signal Away From Long Distance
The transmission or receipt of wifi signals imposes restrictions on all wireless devices. This range is primarily reliant on wireless routers and linked instruments. Wifi is easily accessible through several hack techniques for extra wireless signal. A reflectometer, a wireless extender, frequency reduction, and other gadgets are used throughout this process.
How do long range WiFi networks work?
The nearest individual in a room often receives more excellent signal strength from linked gadgets. The signals weaken as they get further away. The outdoor and point-to-point networks employ powerful and high-gain antennas, extending the bandwidth and improving frequency responsiveness.
Long-range outdoor networks
You can get around any restrictions and extend internet service to your backyard, garden, or camping site. Most people use range extender networks or networks to better signal in an outdoor setting. Although these systems work well, they need to be placed at the proper distance for routers to operate within particular ranges.
Long-range point-to-point networks
A router may reach areas between 200 meters and 200 meters in length under optimal conditions. Typically, this isn’t very helpful for getting to a separate building. Interest Points Internet access may be extended between two building locations using long-range systems. There must be a directional antenna for sending signals into the building and long-range wireless transmissions.
Use WiFi Extender To Receive Signal From A Long Distance
Depending on your connected device, the wifi extender is used as a wireless and ethernet cable router to expand the WiFi range up to 4 kilometers. Using this method to purchase wifi extension devices is simple and required. A wireless range extension device is the least expensive option for the increased wireless range.
How can a WiFi Extender receive signals from a long distance?
A wireless network extension is relatively easy to install. To set up the Extender, log in using an admin username. Because there are just a few quick steps involved, install an extension and add it to the router. We’re confident that we recognize your preferences.
Tell me the best way to buy a long-range wireless network?
Long-range wireless technology relies heavily on antennas. They allow us to communicate across great distances without losing our messages. Antenna type and strength determine signal distance and sensitivity. Before purchasing long-distance WiFi, you should be familiar with antenna choices, strength, and frequency ranges. Considering these characteristics might help you select the best long-range network for your requirements.
Frequency bands
WiFi uses sound frequencies for all of its communication. The 2.4GHz and 5GHz sound frequencies are measured in GHz. The range, speed, and bandwidth between the two GHz bands vary. Although the 2.4GHz band can transmit data over longer distances, it does so at a slower rate. The 5GHz band is much faster but has a smaller coverage area. It is recommended to use the 2.4GHz band when using a WiFi router with extended ranges since the signal will cover a long distance.
How to receive Wifi signals from 1 km or more?
Consider purchasing a long-range wifi extender, such as the TP-link N300, if you wish to get wifi signals even if you are 1 km from a wifi-enabled area. Once you purchase two of these, you may use a line of sight to receive wifi signals up to 4 kilometers away. Long-distance wifi transmission is made possible with the help of this wifi extender. The TP-link N300 uses tdma technology to improve throughput performance.
One of the wifi extenders should first be connected to a router using an Ethernet cable before being extended to an adapter. It is waterproof, so you can even mount it on a telephone pole or flag pole. To have the desired result, you need to understand how to connect them correctly.
Use these extenders, and the signal is weak. You can try boosting it by connecting a parabolic antenna, such as the TL-ant2424b. The welded steel reflector on this antenna is there to boost efficiency.
How to get wifi 5 miles away?
Even when you are far from the source, a super wifi antenna may enable you to pick up powerful wifi signals. This antenna performs exceptionally and can assist in gathering signals from a far distance.
After purchasing the antenna, connect it to your computer. It is a USB device that requires a line of sight to function correctly. Only when there are no obstructions between the stations can a line of sight propagation method receive and transmit data. Additionally, the stations need to be visible to one another.
Along with the excellent wifi antenna, you will also get a 15-foot split cable when you buy it. Using the provided cable tie, you may secure this antenna to a pole outside to get a far signal. This antenna is simple to install and will allow you to receive WiFi signals over great distances. However, contact us if you come across any problems.
Conclusion
Free Wi-Fi can increase your delight in using the internet because everyone enjoys obtaining things for nothing. If someone is far away from you, you might be able to connect with them. Investing in a long-term wireless extender is the best way to establish communication and network connectivity. Consider using a super wifi antenna to get wifi signals from far-off areas.
FAQ:
Is there an app that picks up Wi-Fi from further away?
There isn’t an app that can directly increase the range of your device’s Wi-Fi reception, as Wi-Fi reception depends on the hardware (antenna) and firmware of your device. However, there are ways to improve Wi-Fi connectivity, which include:
Wi-Fi range extenders: These are devices that can be placed between your Wi-Fi router and the area where you need better coverage. They amplify the Wi-Fi signal, effectively increasing the range.
Wi-Fi mesh systems: These are a set of interconnected Wi-Fi routers that work together to provide a seamless and strong Wi-Fi signal throughout your home or office.
High-gain antennas: Replacing your device’s existing antenna with a high-gain antenna can improve Wi-Fi reception, but it’s not always possible, particularly for smartphones and tablets.
Positioning your router: Place your Wi-Fi router in a central location and away from walls or metal objects that may interfere with the signal.
Router firmware update: Make sure your router’s firmware is up to date, as updates may include improvements to Wi-Fi performance.
Wi-Fi analyzer apps: These apps can help you analyze Wi-Fi signal strength, channel interference, and other factors in your environment that may be impacting your Wi-Fi performance. Based on this information, you can make changes to your router settings or adjust the location of your devices for better reception.
How do I receive Wi-Fi signals from 1 km or more?
Install wireless repeaters between the wireless routers and the signal-sending wireless devices. For wireless communications, construct a large directional antenna.
How do you share Wi-Fi with someone far away?
Generally, you can use a mobile hotspot to connect to the internet, connect to several other devices using the network name and password, and join that new network.
Related Articles
Can My Neighbors' WiFi Interfere With Mine?
We understand the importance of fast and reliable internet for homes and businesses. Feel free to check out more tips on our website!
Read moreHow to Get Better Wifi Signal From Neighbor
We understand the importance of fast and reliable internet for homes and businesses. Feel free to check out more tips on our website!
Read moreHow to Extend WiFi to Detached Garage
We understand the importance of fast and reliable internet for homes and businesses. Feel free to check out more tips on our website!
Read more
